I designed the Knowledge Base Management interface for an AI chatbot project to help support human agents resolve cases faster, by restructuring records into AI-ready formats.
Primary Role: UX Design Lead, Time frame: Feb. 2025 – June 2025
About the Project
The KB (Knowledge Base) Management Feature Design is an essential part of our software project—an AI chatbot developed to support technical support agents (users), for a smart TV subscription product. This AI chatbot acts as a secondary tool, allowing agents to input specific details of a case or ticket, which the AI chatbot then analyzes to deliver quick and accurate information for resolution. The feature is designed to restructure existing knowledge base records into a format optimized for AI systems. This ensures seamless interaction between agents and the chatbot, enabling efficient troubleshooting and enhanced support capabilities.
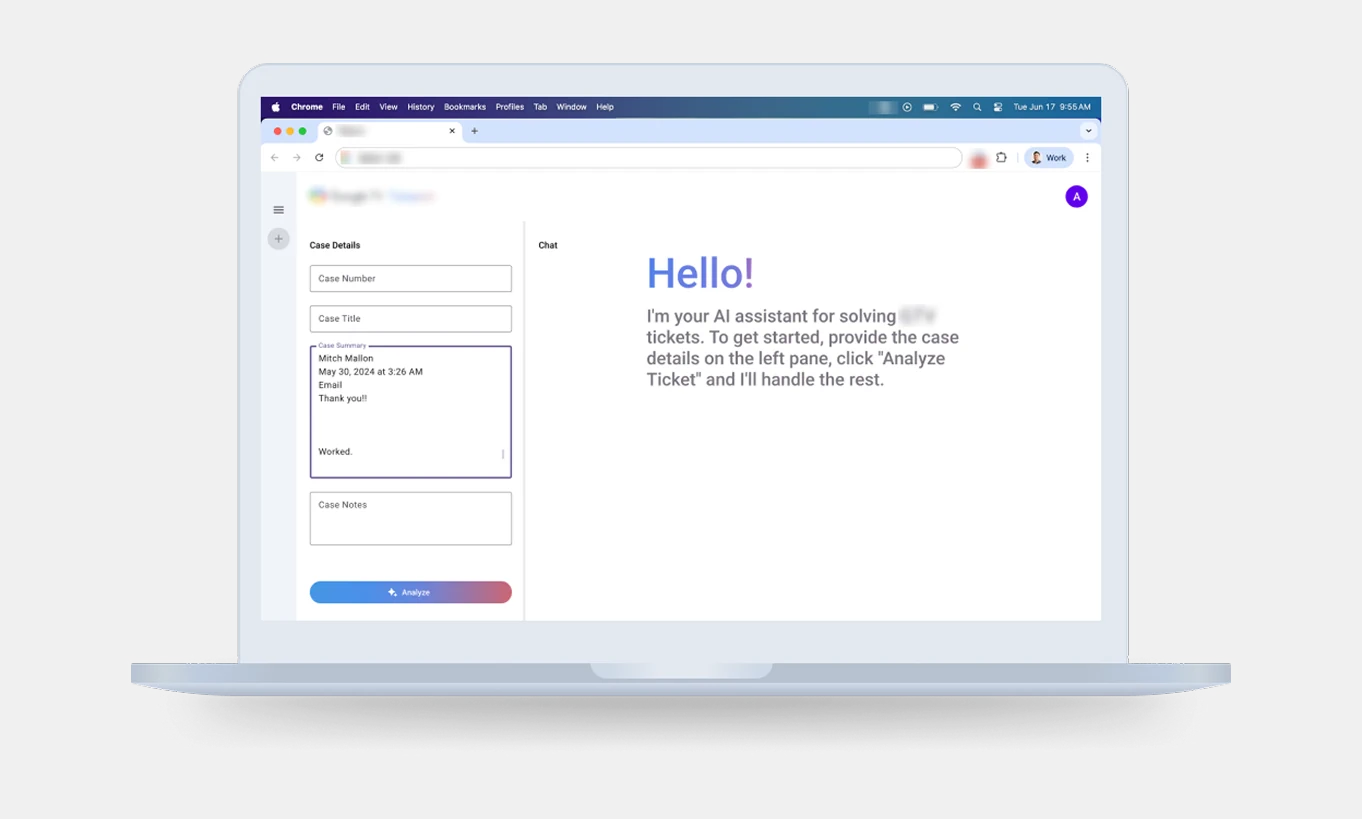
AI chatbot UI
Objective
The primary objective is to address inefficiencies in the manual KB documentation process, ensuring that KB content is structured for AI compatibility. This enables the AI chatbot to provide accurate and context-aware responses to technical support agents, ultimately enhancing the customer experience for smart TV users.
Problem Statement
“Technical support agents face challenges in documenting KBs due to tedious and manual processes. These inefficiencies hinder the AI chatbot’s ability to retrieve and process relevant information effectively. “
Key issues include:
• Misalignment of fields during manual input.
• Limited options for embedding complex data formats (e.g., media, sub-content).
• Usability frictions when adding, formatting, and embedding non-textual content.
Old Knowledge Base Tracker
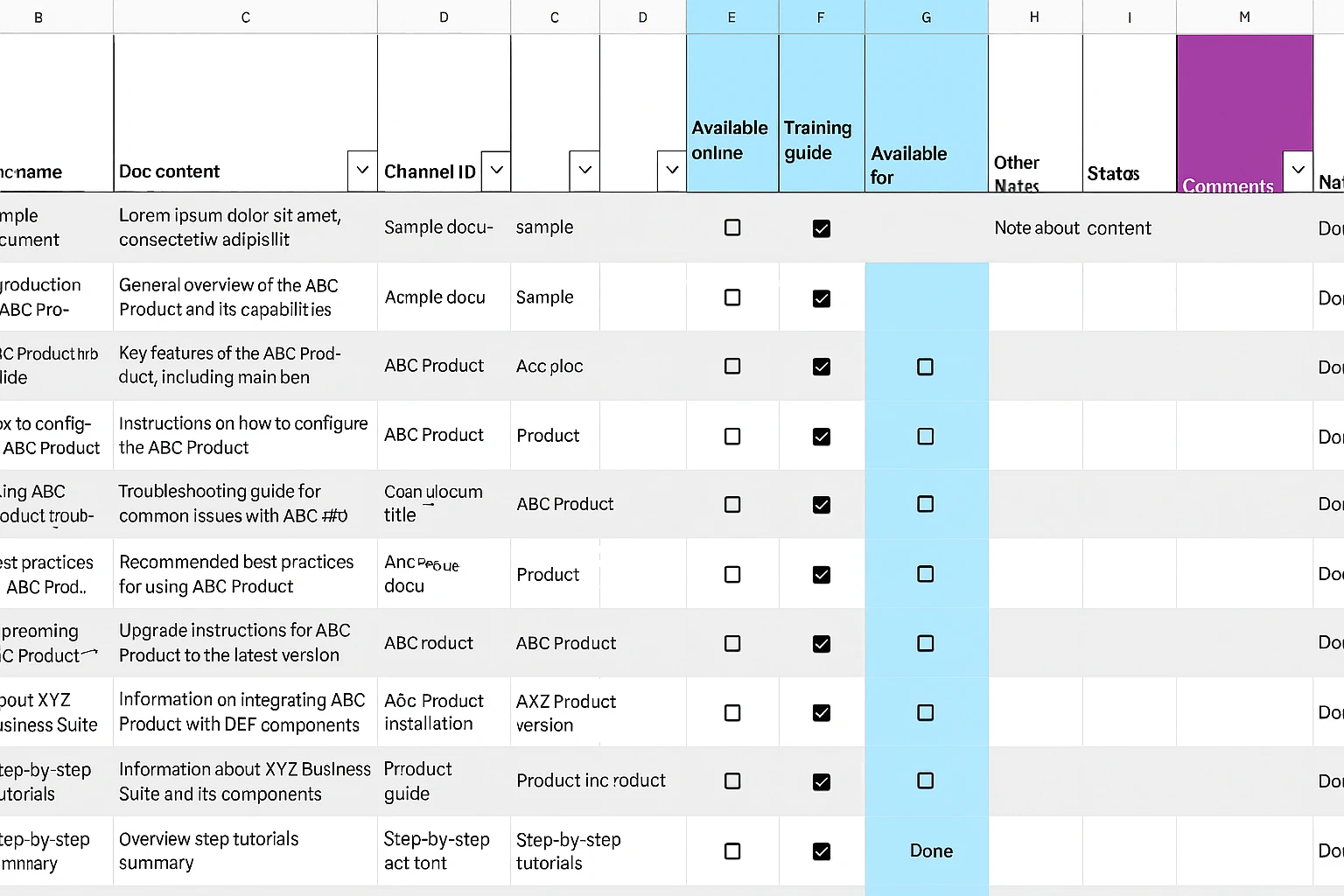
Knowledge base entries were first logged manually by agents in spreadsheets, then bulk-copied by engineers into the chatbot’s database.
KB Data Structure
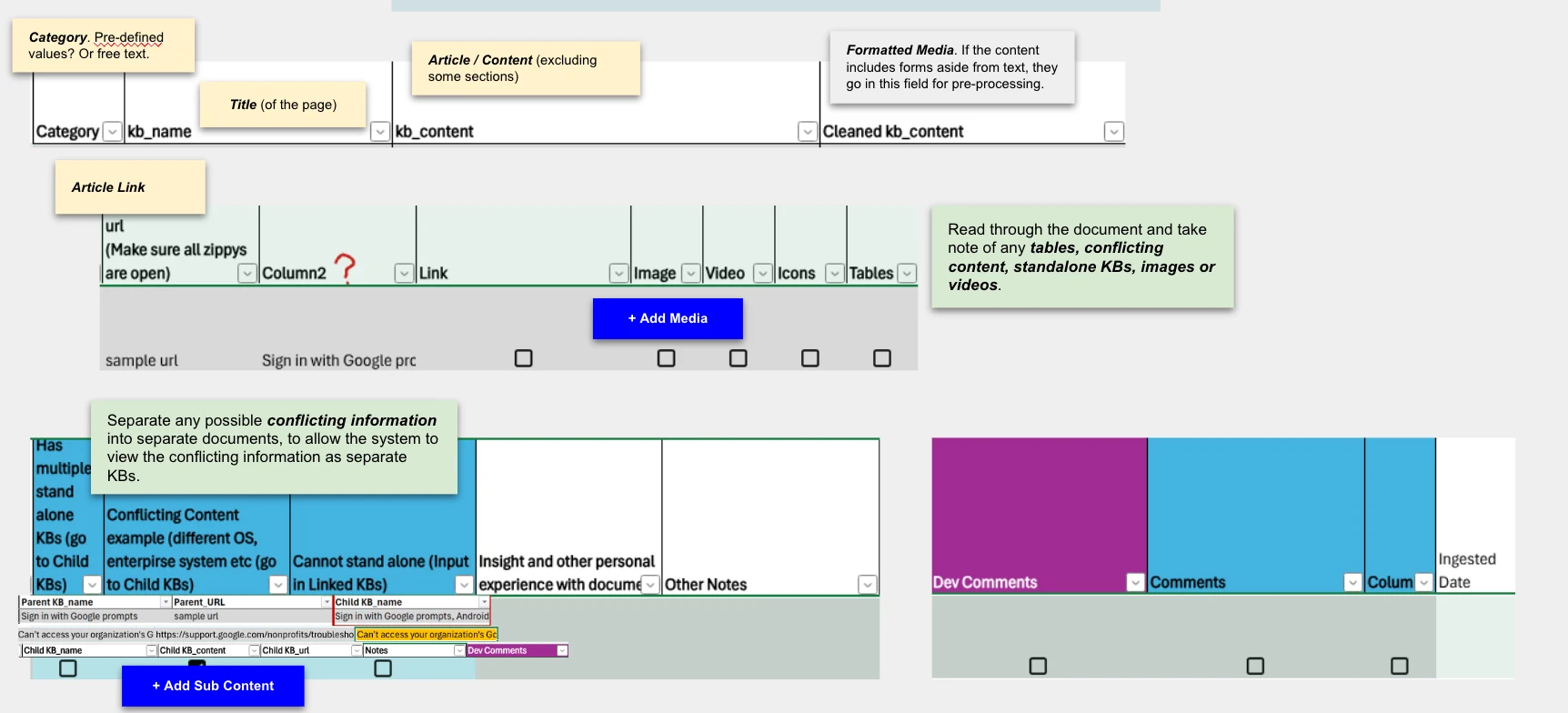
To ensure the AI chatbot can effectively utilize KB data, the following attributes were defined:
Primary Attributes:
Category
Title
Article/Main Content
Formatted Media
Article Link
Additional Attributes:
Media (e.g., images, videos, tables)
Child KBs/Sub-content (used to separate conflicting or nested information)
These attributes ensure that the AI chatbot can process structured data for accurate and contextually relevant responses.
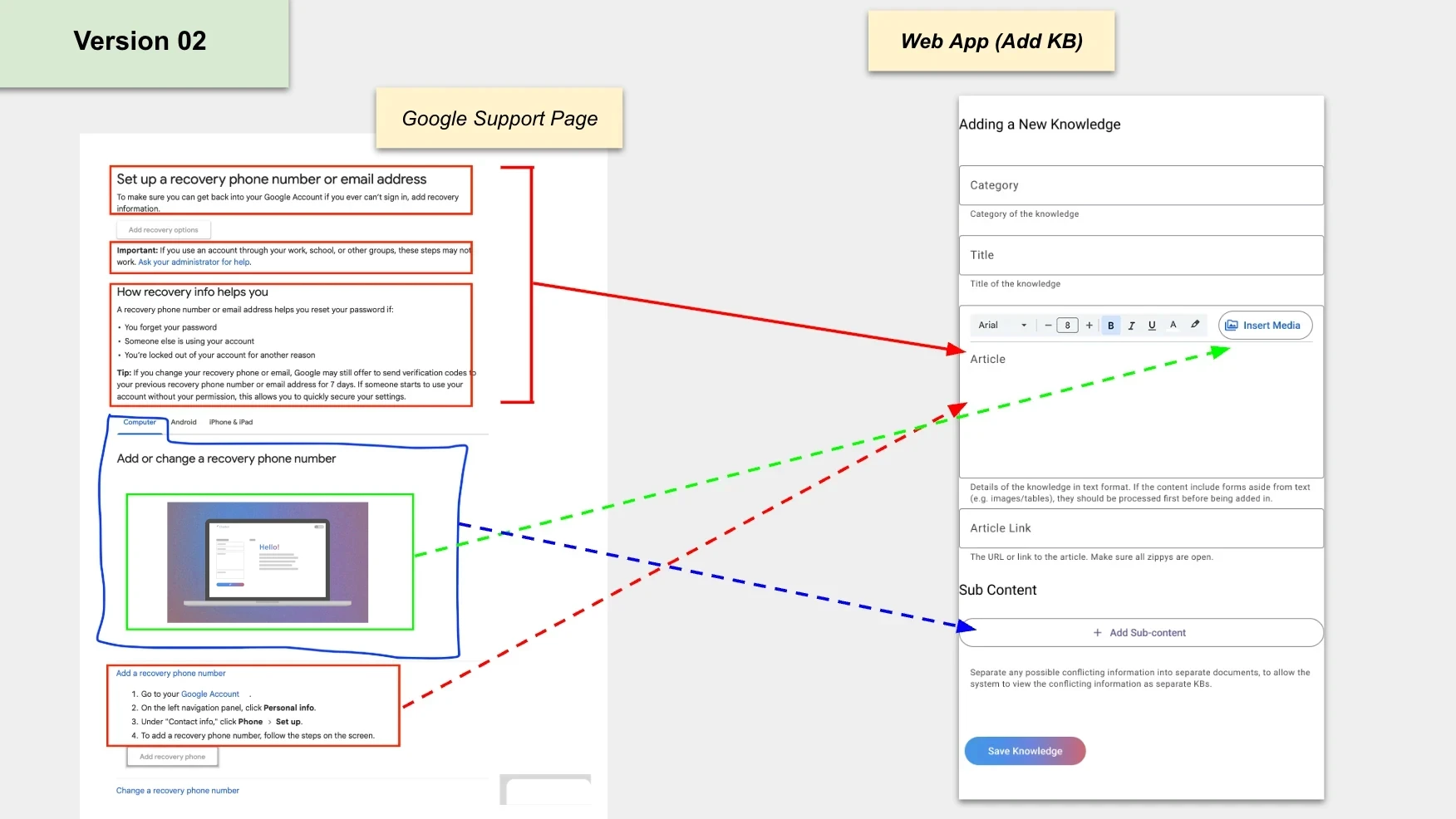
Adding of KBs (as is)
The following image shows how content from public help pages is mapped into the KB tracker by the users (agents).
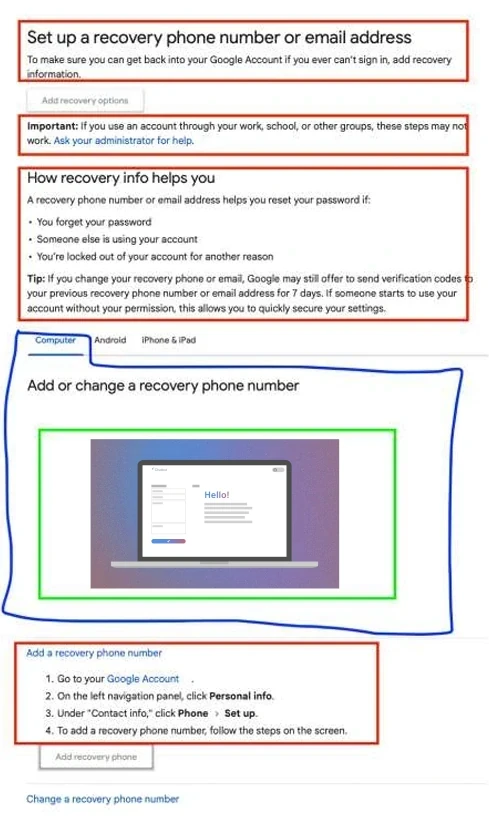
• Article/ Main Content in red
• Child KBs / sub-content in blue (to separate any possible conflicting information into separate documents)
• Media (images, video, tables) in green.
Proposed Design Process
The design process involved iterative improvements across three (3) versions, each addressing specific challenges and incorporating feedback to enhance the LLM's performance.
Version 00: Initial Concept
• Basic web form fields introduced:
• KB Name, Category, Content, File Upload.
• Simplified input approach but lacked alignment with actual KB data structure, limiting the LLM's ability to process data effectively.
The design process of this concept took place before the data engineering team introduced to us the actual KB data structures.
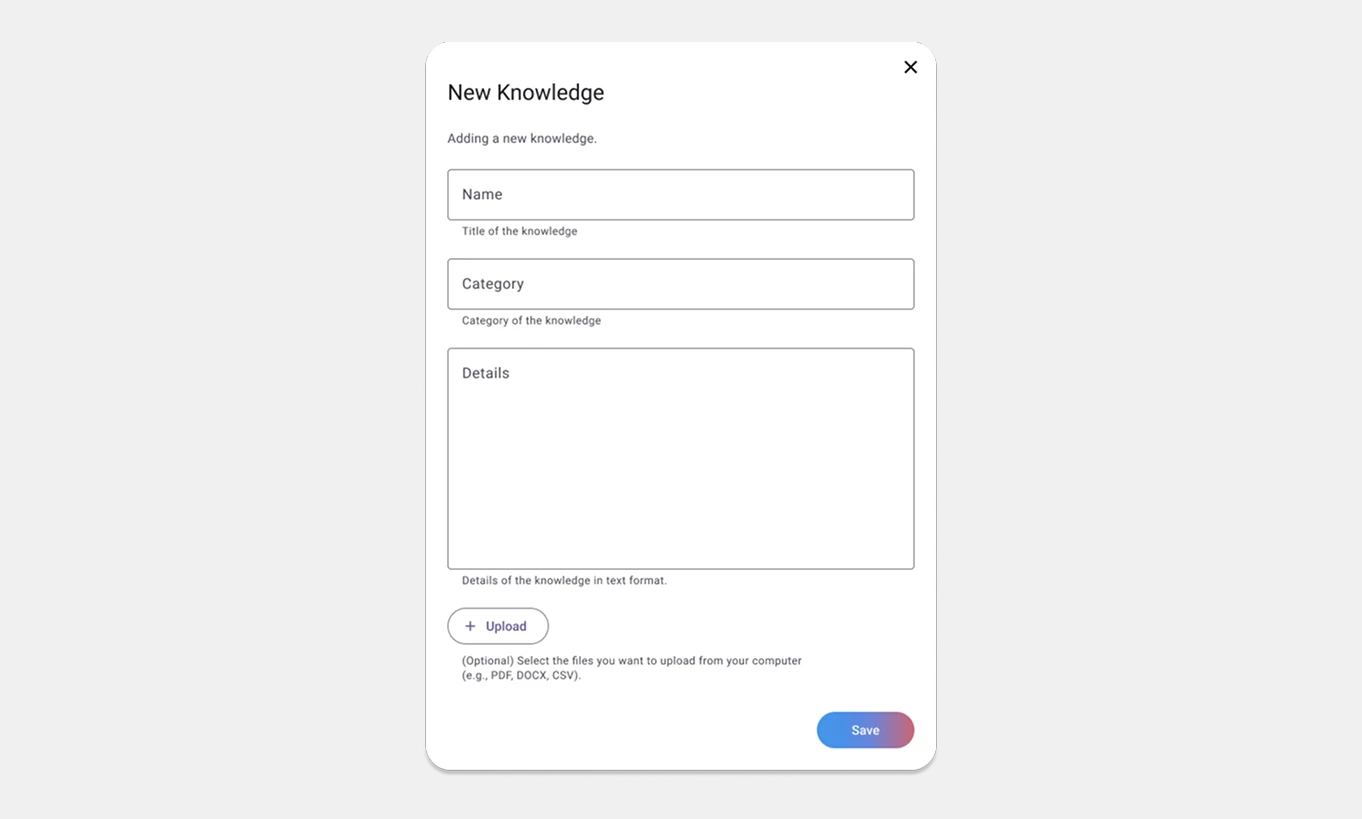
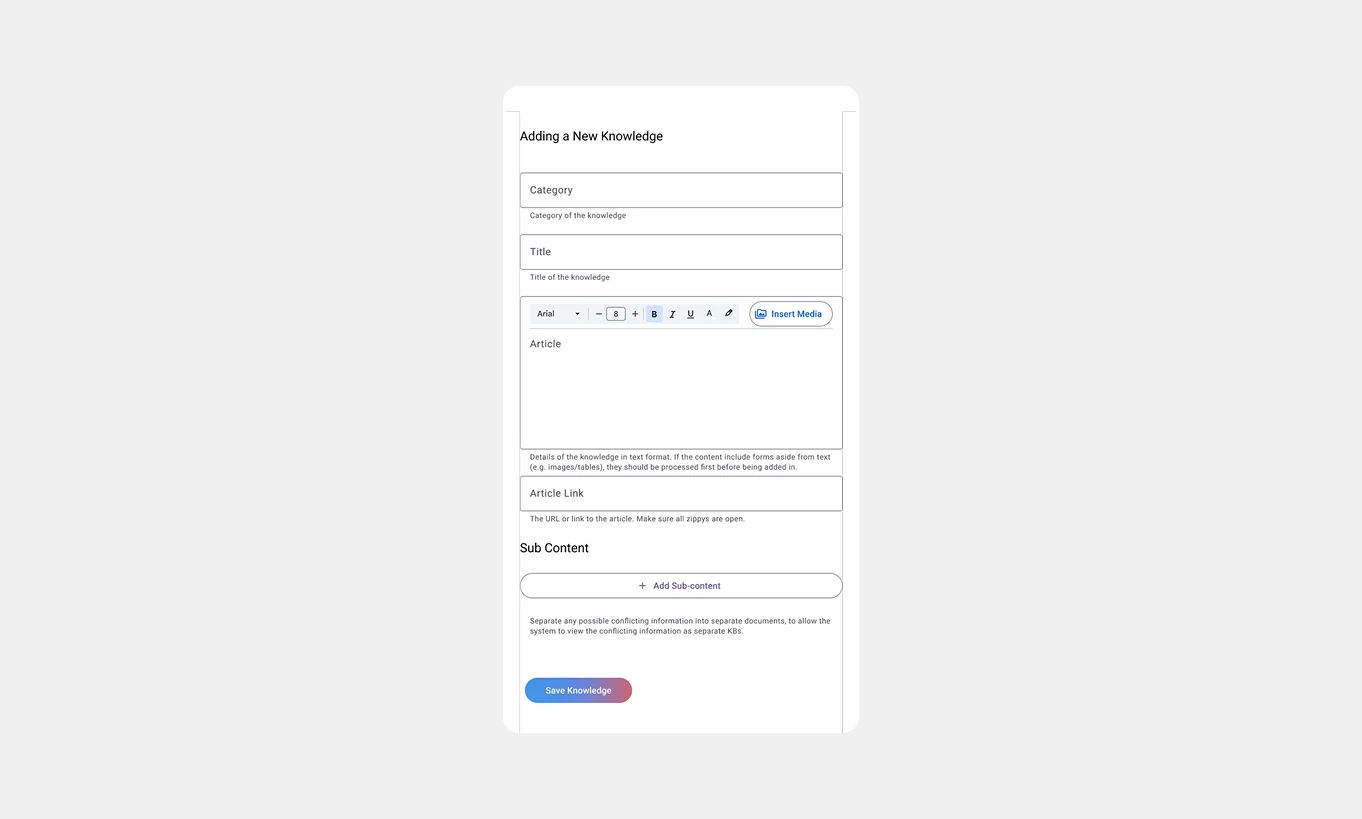
Version 01: Enhanced Structure
Adjusted form fields to align with KB tracker attributes: Category, Title, Content/Article, Article Link, Media, and Sub-content.
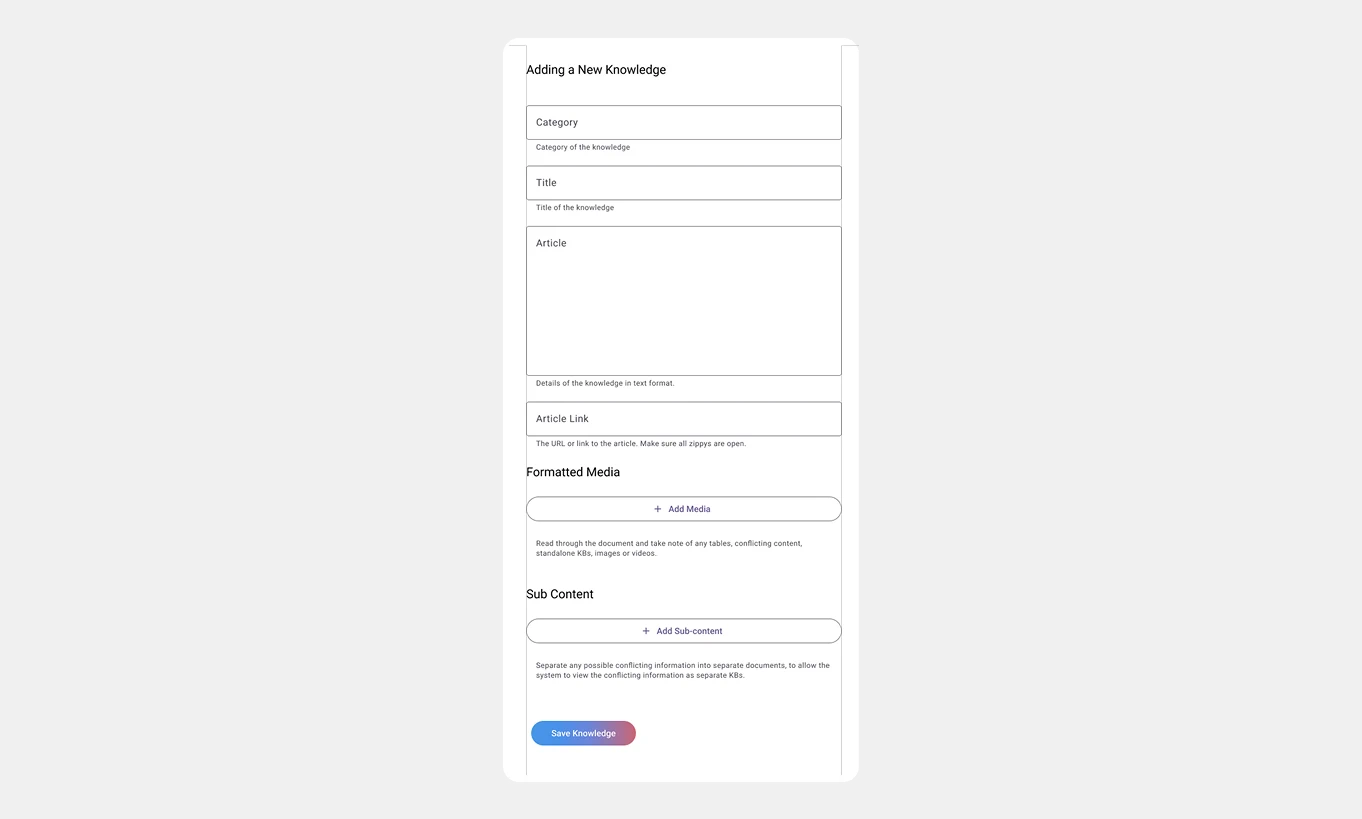
New components added:
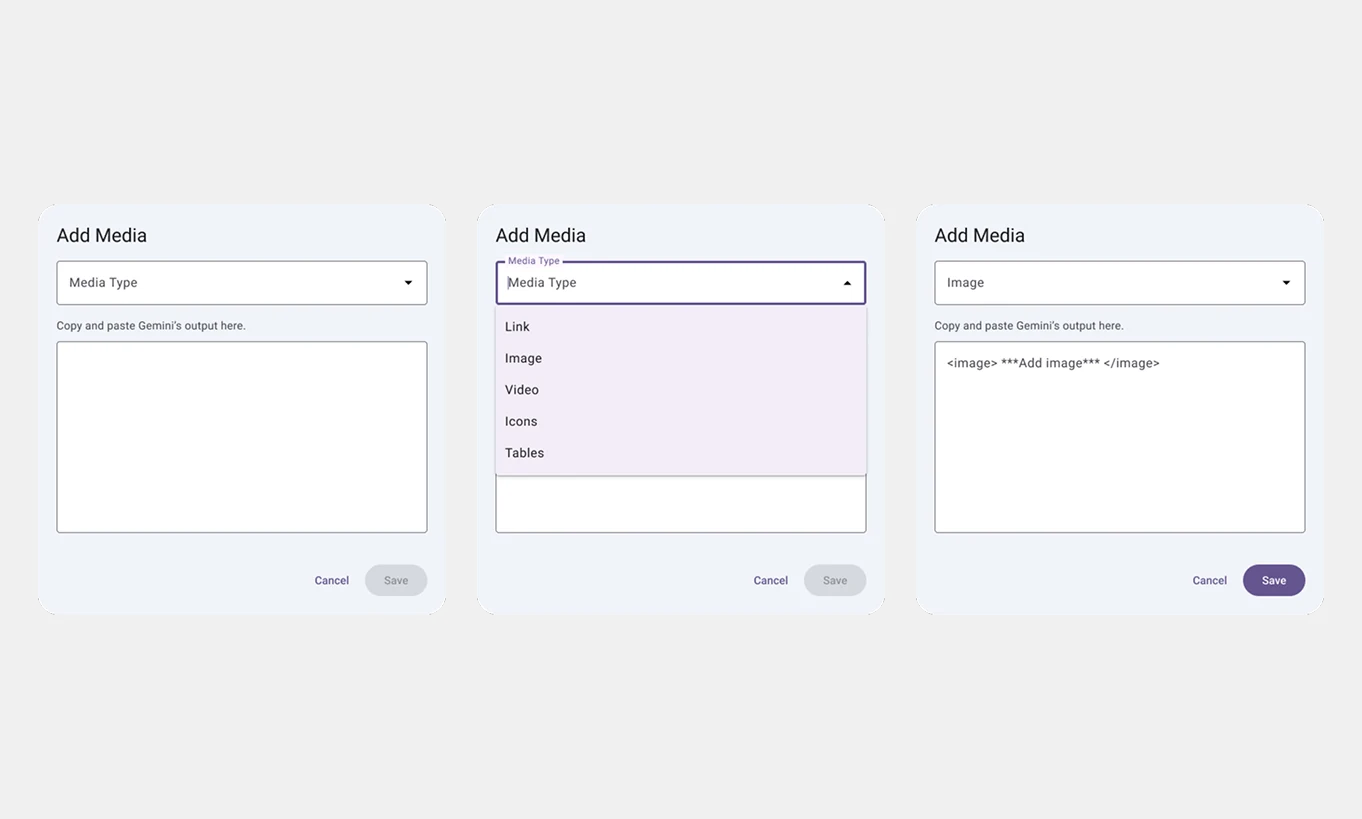
1. Add Media Button: Shows a pop-up form that allows users to upload and format various media types.
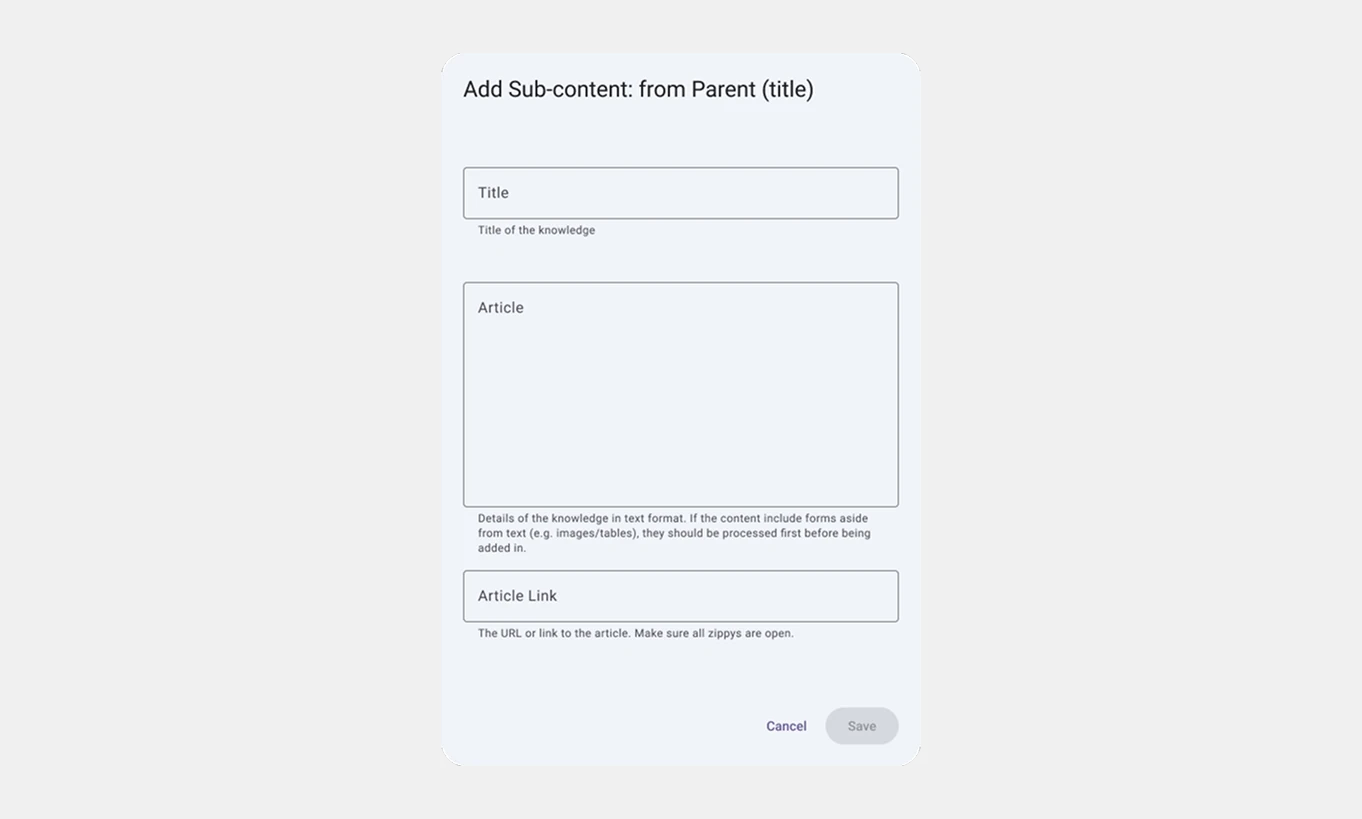
2. Add Sub-content Button: Pop-up form with fields to input child KBs.
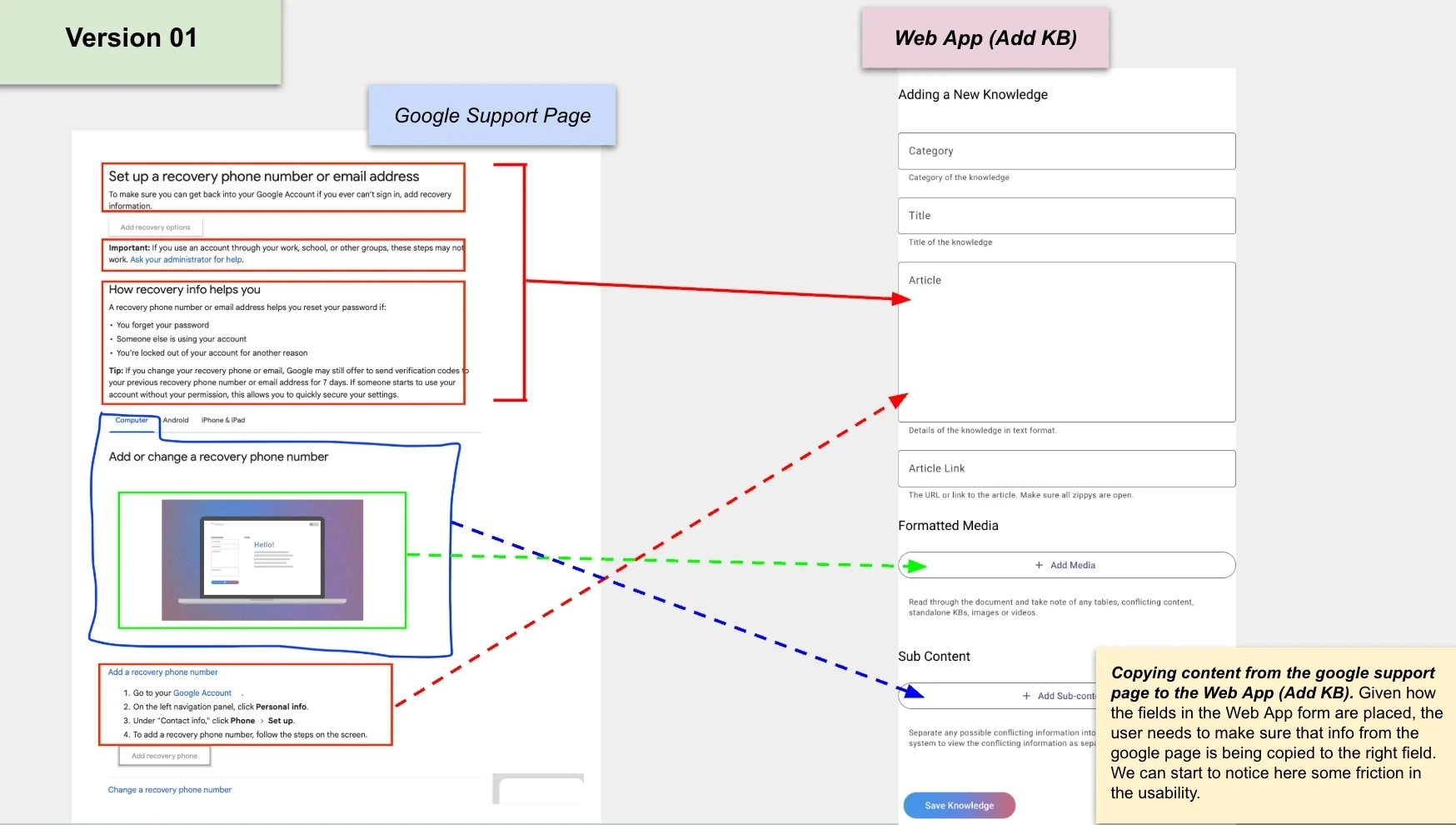
Copying content from the support help pages to the KB management tool. Given how the fields in the tool are placed, the user needs to make sure that information from the source is being copied to the appropriate field. We can start to notice here some friction in the usability.
Version 02: Inline Media Integration
Inline Media Embedding: The article field allows users to integrate media directly inside the text area.
Options for media selection and insertion (e.g., image, video, tables).
Improved guidance ensured proper copying of external content to appropriate fields (e.g., Images must be pre-formatted in ChatGPT before pasting in the field).
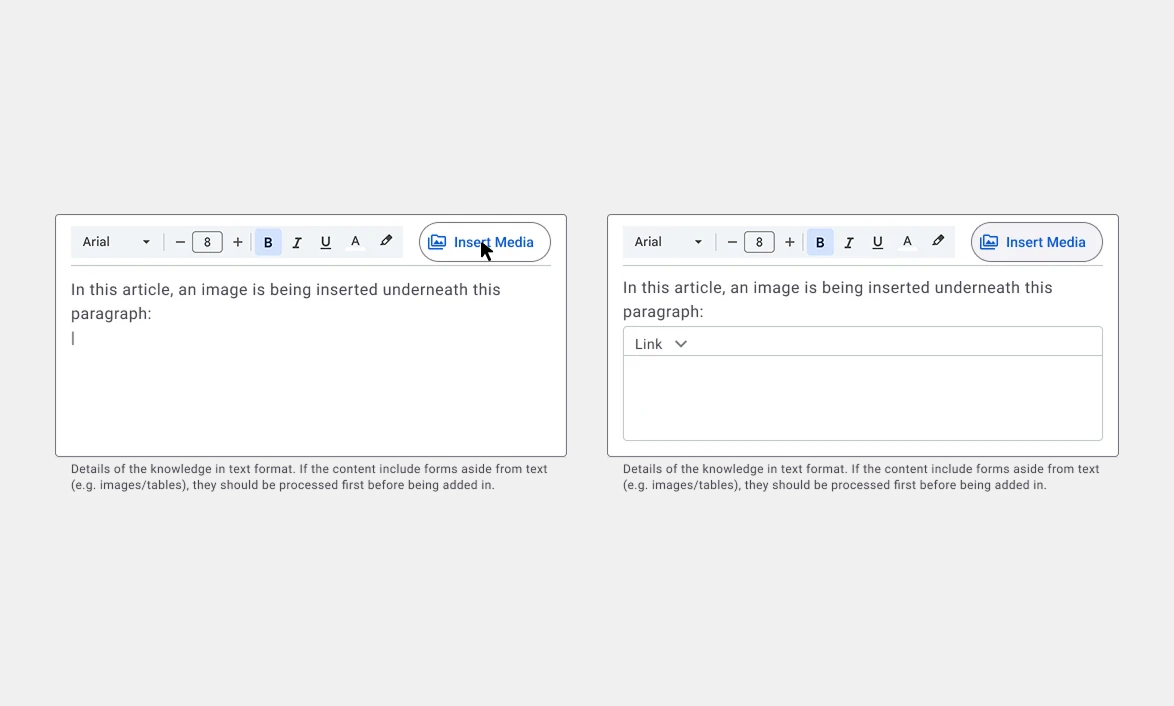
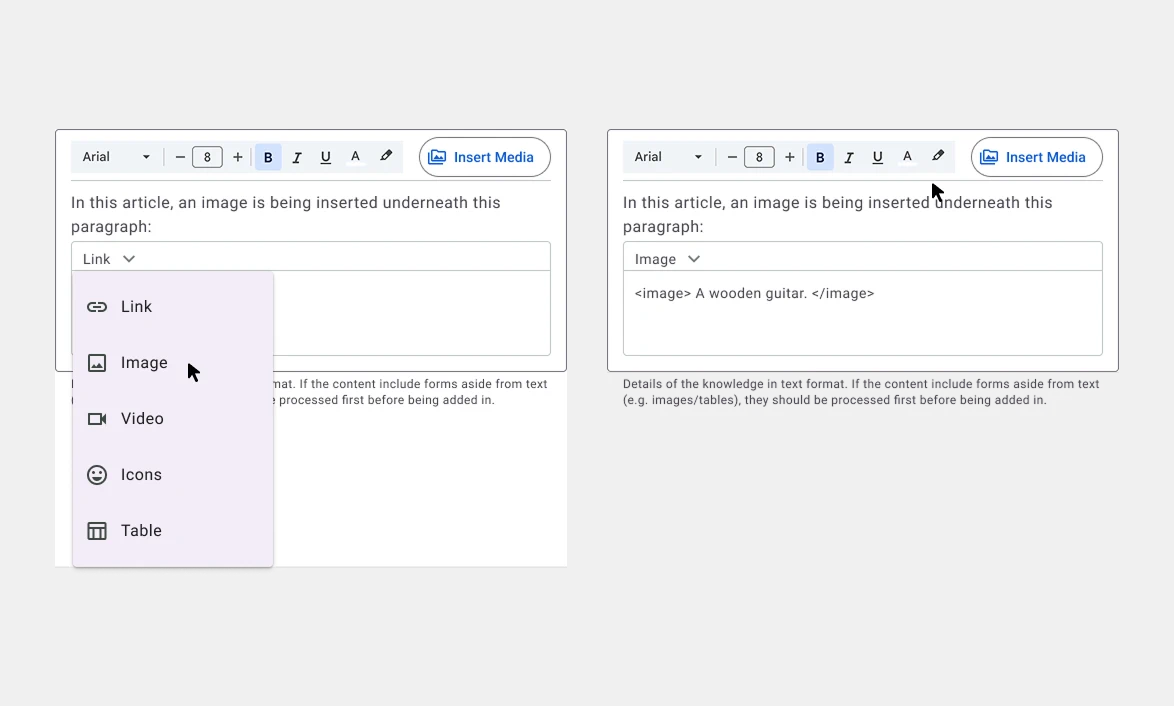
The dynamic fields appear as embedded elements within the article field making them truly part of the message field.
Copying content from support page to KB tool. Even in this revision, usability issues might still be present.
Version 03: Final Iteration
Media & Sub-content Integration: Embedded directly within the main article field, mimicking blog post workflows.
Article Field. The following screens show how the inserting of media and sub-contents are being done inside the article field.
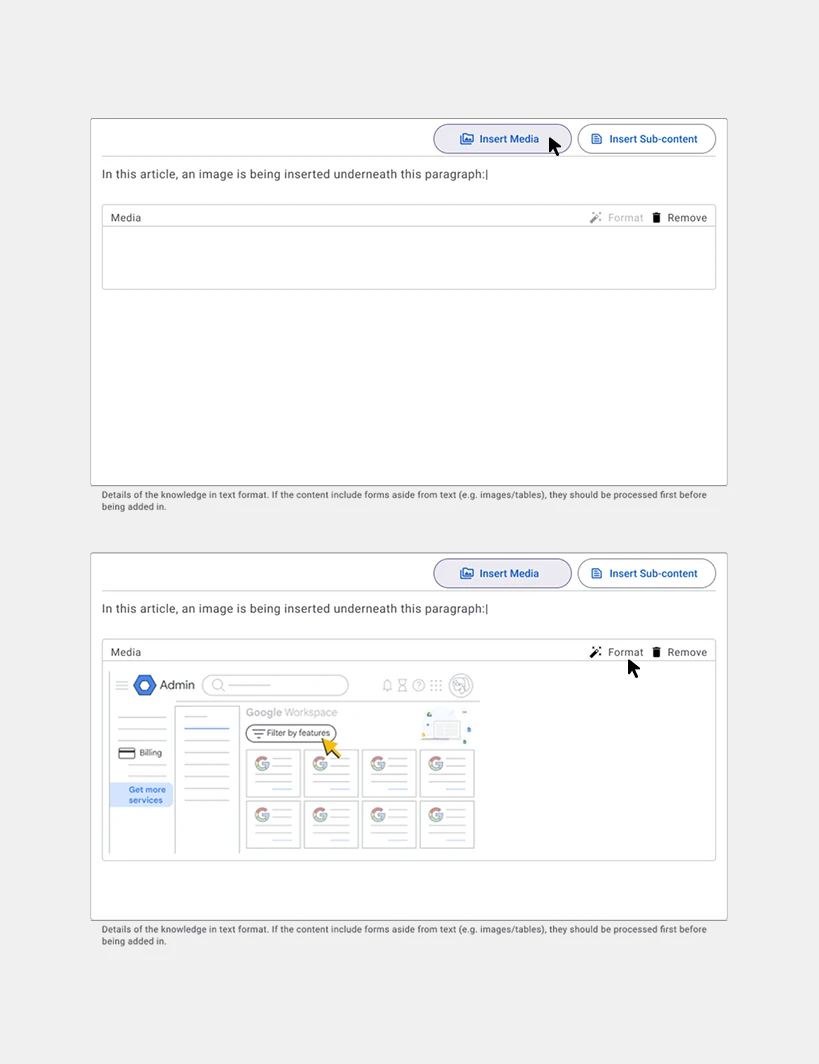
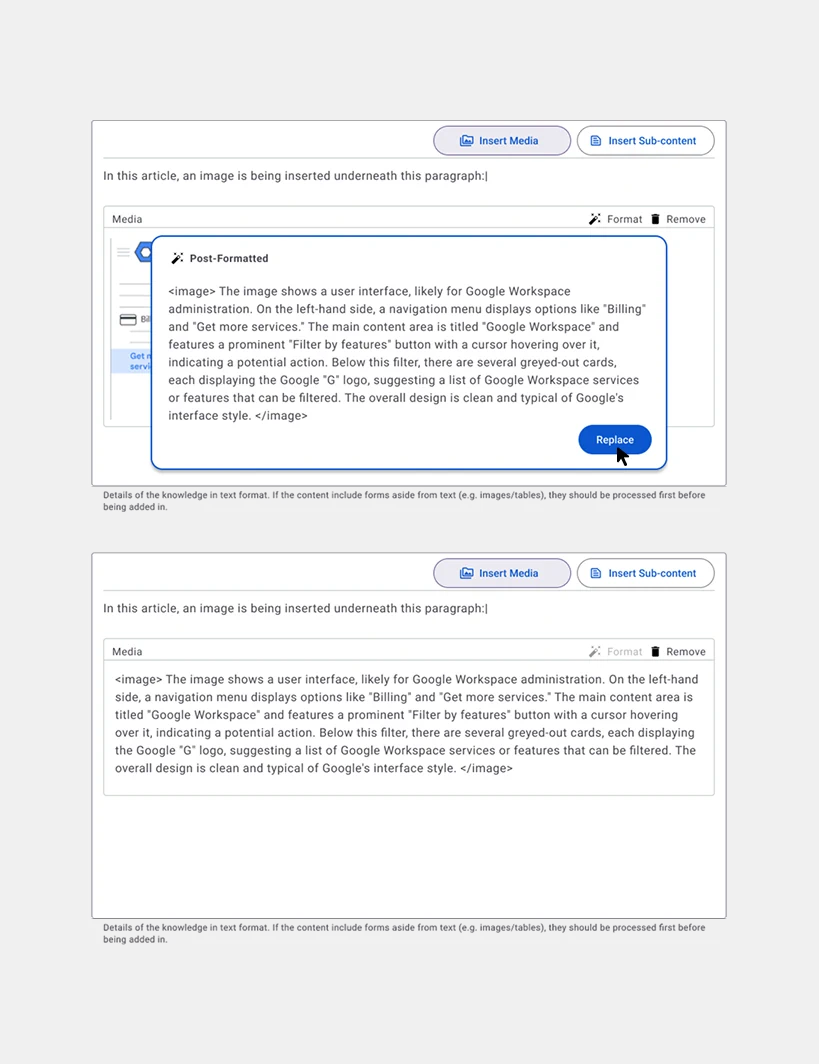
Formatting for non-Text Media. Media converted into text-based formats for AI compatibility.
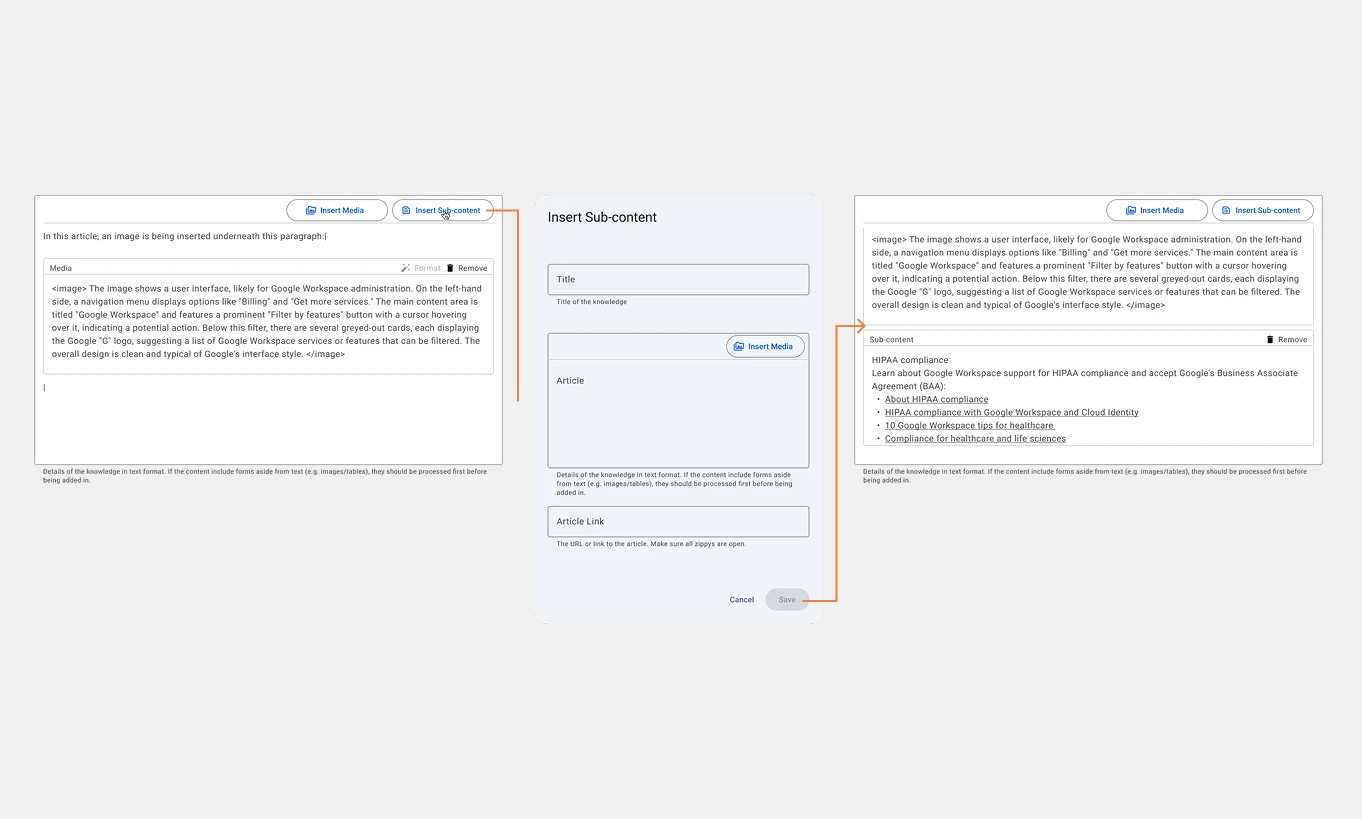
A pop-up window to input sub content data. Inserting non-text media is also enabled in this form.
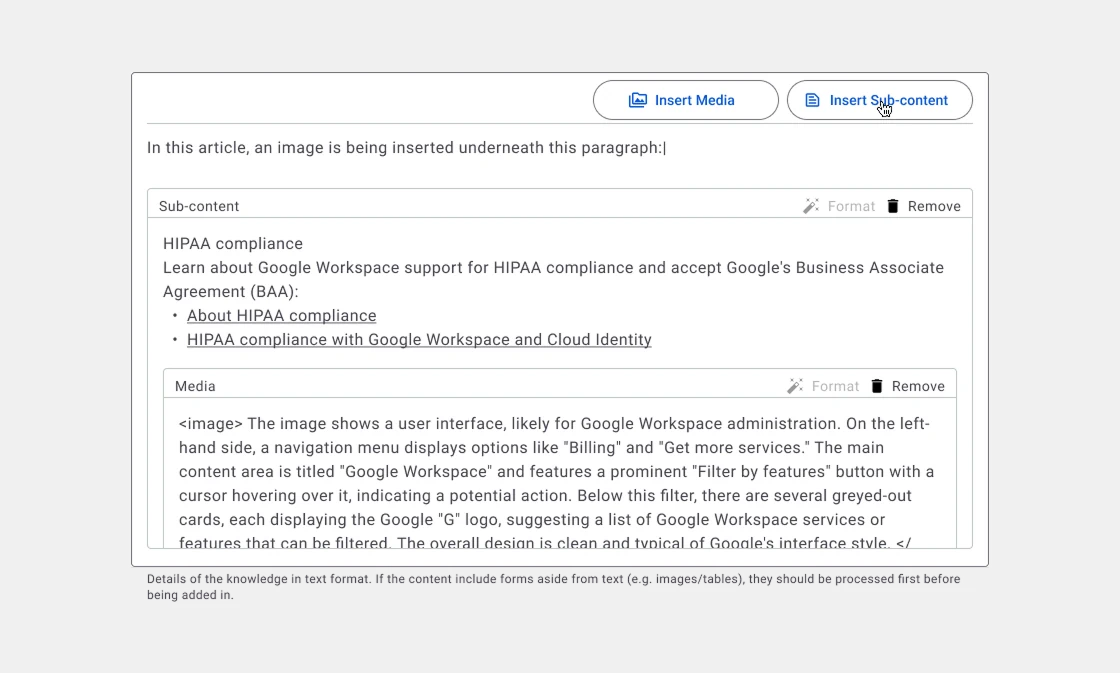
Shown here the 'Article' field displays a two-level insertion structure: media embeddings within a sub-content.
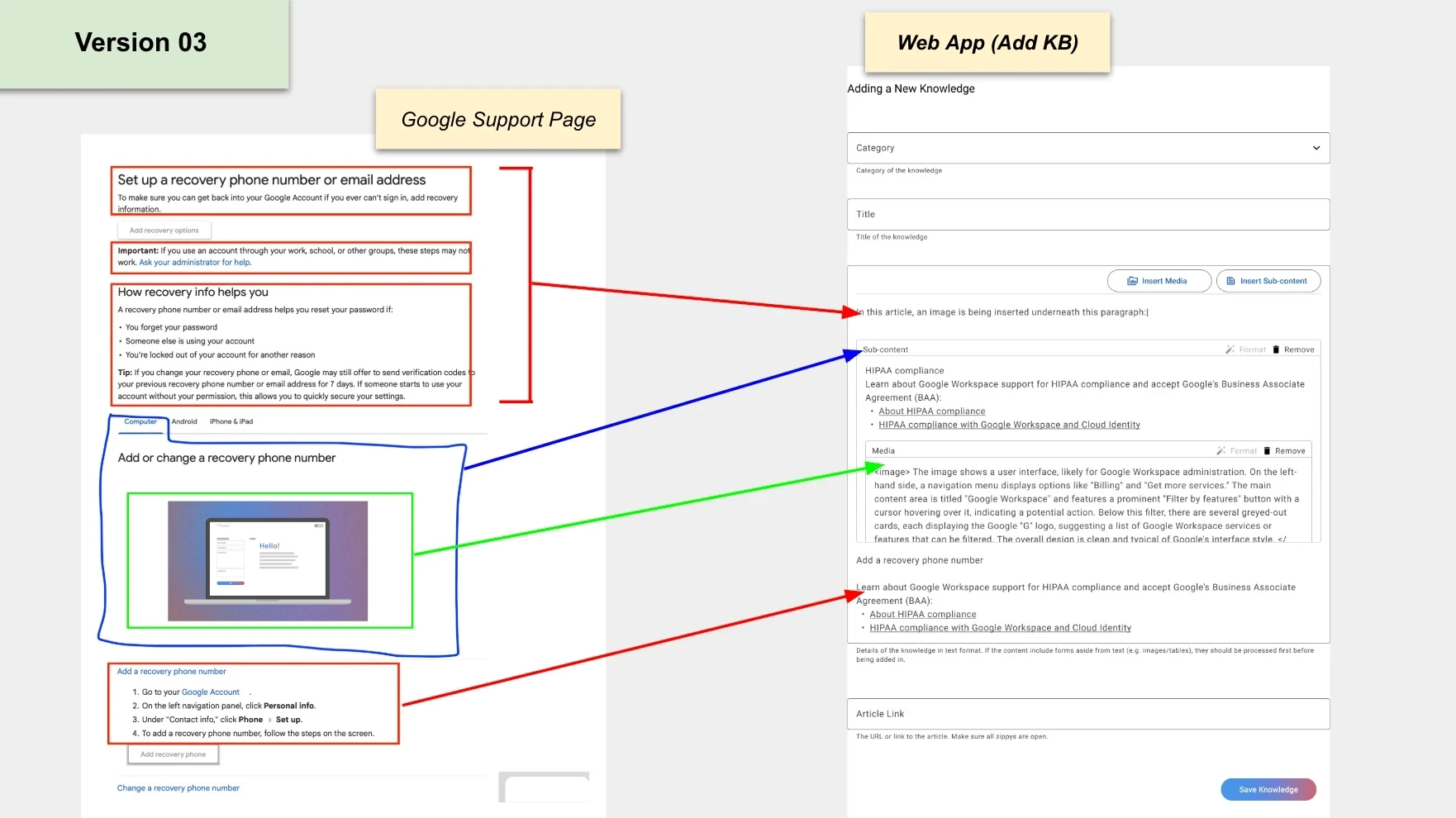
Final version. This version introduces usability enhancements, enabling seamless copying content from help pages to the KB tool, with fields now populating in a linear sequence.
Usability Insights
Key usability improvements included:
✓ Reduction of cognitive load for users in mapping data fields.
✓ Seamless workflows for embedding rich media within a text-first database.
✓ Frictionless processes for adding child KBs and managing supplemental content.
These enhancements ensure that the AI chatbot can retrieve and process KB data efficiently, providing accurate and timely support for smart TV users.
Impact
The redesigned system significantly enhances:
• Data Structuring: Ensures KBs are AI-ready for the LLM.
• Agent Productivity: Simplifies and accelerates the KB documentation process.
• Customer Experience: Enables the AI chatbot to provide accurate, context-aware responses, improving the overall support experience for smart TV users.
Conclusion
The iterative process of KB Management Feature Design successfully delivers a user-friendly interface that aligns with AI prioritization for text-based retrieval systems. This feature is a cornerstone of the AI chatbot project, ensuring that technical support agents can efficiently assist smart TV users. Future enhancements may focus on automation (e.g., directly importing structured content) and advanced AI-based content validation to ensure higher accuracy.
Share this story
About the Author
Bryan Alipar
Founder, Creative Director at Hatchbloc
Passionate about business, design, and digital marketing. With a keen eye for detail and boundless creativity, Bryan offers a unique perspective on the fusion of aesthetics and strategy in the corporate landscape. When not dissecting business trends, he explores nature, fueled by his love for travel, music production, and coffee.


